Contents
Summary
The command
\convertnumber
is used to typeset a number in a specific format.
Settings
| \convertnumber{...}{...} | |
| {...} | empty default none month month:mnem character Character characters Characters a A Numbers word words Word Words n N romannumerals Romannumerals i I r R KR RK greek Greek g G abjadnumerals abjadnodotnumerals abjadnaivenumerals hebrewnumerals yiddishnumerals thainumerals devanagarinumerals gurmurkhinumerals gujaratinnumerals tibetannumerals greeknumerals Greeknumerals arabicnumerals persiannumerals arabicexnumerals arabicdecimals persiandecimals koreannumerals koreanparentnumerals koreancirclenumerals kr kr-p kr-c chinesenumerals chinesecapnumerals chineseallnumerals cn cn-c cn-a sloveniannumerals slovenianNumerals spanishnumerals spanishNumerals russiannumerals russianNumerals mathgreek set␣0 set␣1 set␣2 set␣3 continued zero name |
| {...} | number |
| Option | Explanation |
|---|---|
| month | long month name |
| month:mnem | short month name |
| character | alias for characters |
| Character | alias for Characters |
| characters | lowercase latin characters |
| Characters | uppercase latin characters |
| a | alias for characters |
| A | alias for Characters |
| Numbers | arabic numbers |
| word | alias for words |
| words | literal words: one, two, three ... |
| Word | alias for Words |
| Words | literal words: One, Two, Three ... |
| n | alias for Numbers |
| N | alias for Numbers |
| romannumerals | lowercase roman numerals |
| Romannumerals | uppercase roman numerals |
| i | alias for romannumerals |
| I | alias for Romannumerals |
| r | another alias for romannumerals |
| R | another alias for Romannumerals |
| KR | alias for RK |
| RK | smallcapped roman numerals |
| greek | lowercase greek characters |
| Greek | uppercase greek characters |
| g | alias for greek |
| G | alias for Greek |
| kr | alias for koreannumerals |
| kr-p | alias for koreanparentnumerals |
| kr-c | alias for koreancirclenumerals |
| cn | alias for chinesenumerals |
| cn-c | alias for chinesecapnumerals |
| cn-a | alias for chineseallnumerals |
| mathgreek | mathematical greek (math italic lowercase) |
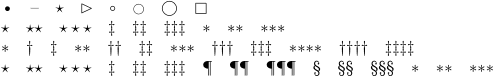
| set␣0 | symbols [bullet, dash, star, triangle ...] |
| set␣1 | symbols [*, **, ***, dag, ...] |
| set␣2 | symbols [*, dag, ddag, **, dagdag ...] |
| set␣3 | symbols [*, **, ***, ...] |
| continued | indicates that a "set" conversion should continue instead of restart |
| name | any conversion defined using \defineconversion |
| number | an actual number |
Description
The command
\convertnumber
is used to typeset a number in a specific format: convert a number into a different form, e.g. to Roman numerals, bullets, etc.
Examples
Built-in conversion set demo
-
\dorecurse {8}{\convertnumber{set 0}{#1}\quad}\par \dorecurse {9}{\convertnumber{set 1}{#1}\quad}\par \dorecurse{12}{\convertnumber{set 2}{#1}\quad}\par \dorecurse{15}{\convertnumber{set 3}{#1}\quad}\par
-